|
alm2cl*
This routine computes the auto (or cross) power spectra of a one (or two) sets of spherical harmonics
coefficients alm.
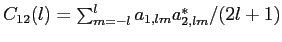
Location in HEALPix directory tree:
src/f90/mod/alm_tools.f90
FORMAT call alm2cl*(
nlmax, nmmax, alm1, [alm2,] cl
)
ARGUMENTS
| name & dimensionality |
kind |
in/out |
description |
|---|
| |
|
|
|
|
nlmax |
I4B |
IN |
the maximum l value used for the alm. |
| nmmax |
I4B |
IN |
the maximum m value used for the alm. |
| alm1(1:p, 0:nlmax, 0:nmmax) |
SPC/ DPC |
IN |
First set of alm values. p
is 3 or 1 depending on wether polarisation is included or
not. In the former case, the first index runs from 1 to 3 corresponding to (T,E,B). |
| alm2(1:p, 0:nlmax, 0:nmmax) (OPTIONAL) |
SPC/ DPC |
IN |
Second set of alm
values. |
| cl(0:nlmax,1:d) |
SP/ DP |
OUT |
resulting auto or cross power spectra.
If both alm1 and alm2 are present, cl will
be their cross power spectrum. If only alm1 is present,
cl will be its power spectrum.
If d=1, only the temperature spectrum
ClT will
be output. If d=4 and p=3, the output will be ClT, ClE,
ClB,
ClT x E, and if 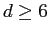 and p=3,
ClT x
B
ClE x B will also be output. and p=3,
ClT x
B
ClE x B will also be output. |
EXAMPLE:
lmax = 128 ; mmax = lmax
call alm2cl(lmax, mmax, alm1, cl_auto)
call alm2cl(lmax, mmax, alm1, alm2, cl_cross)
cl_auto will contain the (auto) power spectrum of the alm coefficients alm1 up to l= 128,
while cl_cross will be the cross power spectra of the two sets of alm coefficients alm1 and alm2.
MODULES & ROUTINESThis section lists the modules and routines used by alm2cl*.
-
none
RELATED ROUTINESThis section lists the routines related to alm2cl*
-
map2alm
- routine extracting the alm
coefficients from a HEALPix map
-
create_alm
- routine to generate randomly
distributed alm coefficients according to a given power spectrum
Eric Hivon
2010-06-18
|

|